Accessing Data from External Clients (QGIS)
Install QGIS Desktop
Open the
Ubuntu Softwareapp
Click
CTRL + Fand search forqgis, click on theQGIS Desktopicon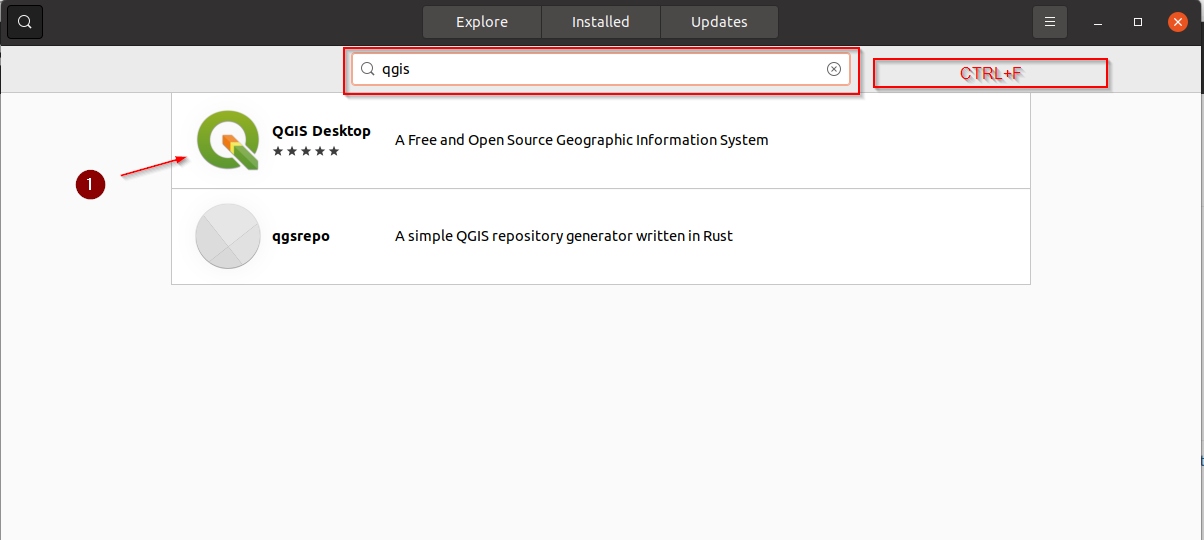
Click on
INSTALLand wait for the process to finish
Once the app has been installed, open it by clicking on the icon

Connect through BASIC Auth
This is the easiest way to connect the client to GeoNode:
- Pros: very easy to configure
- Cons: it always uses a fixed user and you need to change it anytime if you want to switch user
Let’s add a
VECTORIALlayer accessible totest_user1to the client. Click onLayer > Add Layer > Add WFS Layer...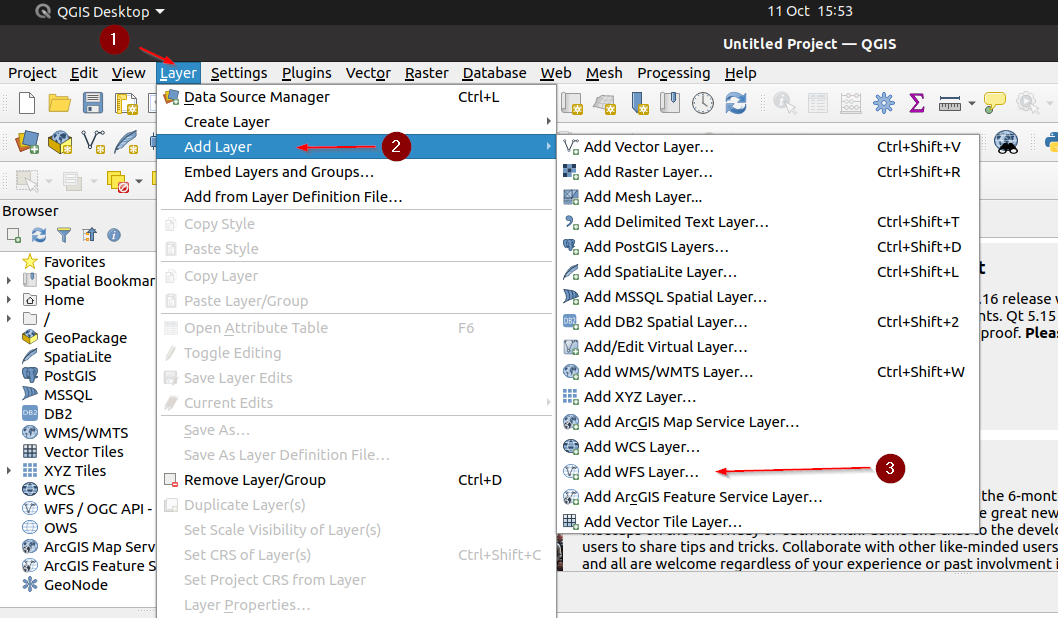
Create a
New Connection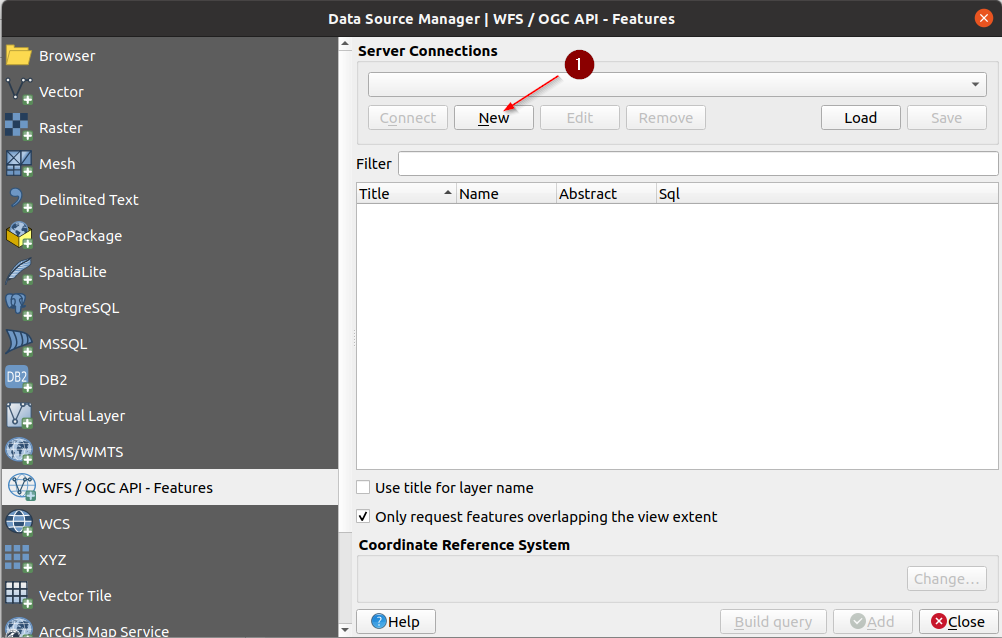
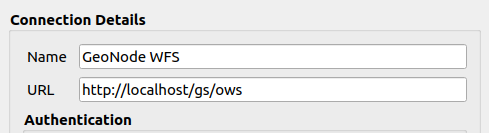
Provide a name, e.g.
GeoNode WFS, and the following URL:http://localhost/gs/ows
IMPORTANT: It is mandatory to pass through the GeoNode proxy
/gs/instead of hitting the GeoServer endpoint directlyIf the client asks for a
NEW master passwordyou can provide any one (e.g.geonode)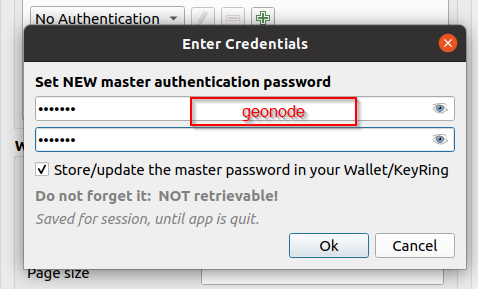
Switch to
Basicauthentication, provide thetest_user1credentials, and click onConvert to configuration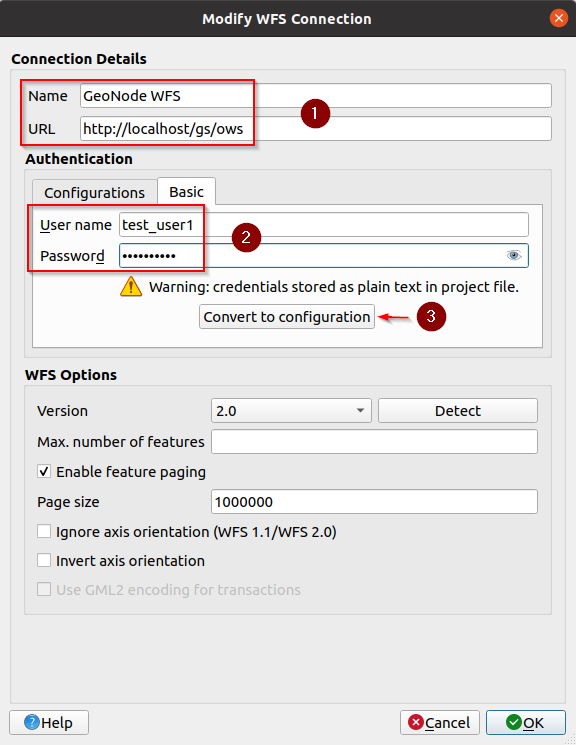
Make sure the converted configuration is selected and click on
Detectto verify that it works. Click onOKwhen finished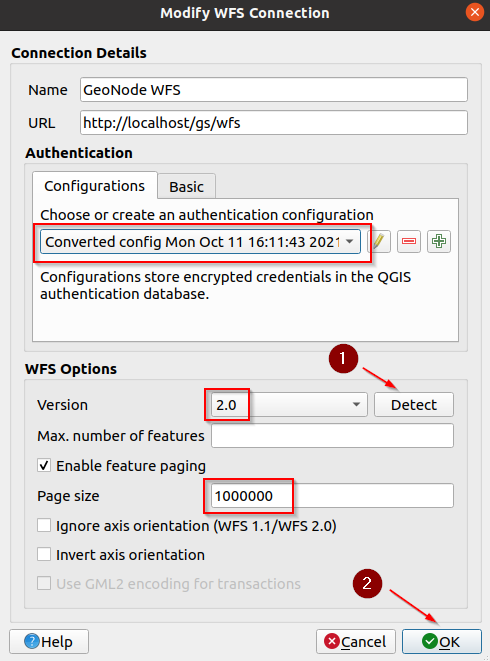
Connect through OAuth2
This is the easiest way to connect the client to GeoNode:
- Pros: it redirects to GeoNode to authenticate, so you can use any login provided by GeoNode
- Cons: difficult to configure
We need to prepare GeoNode first, as an
admingo to theAdmin Dashboardand look forDjango OAuth Toolkit > Applications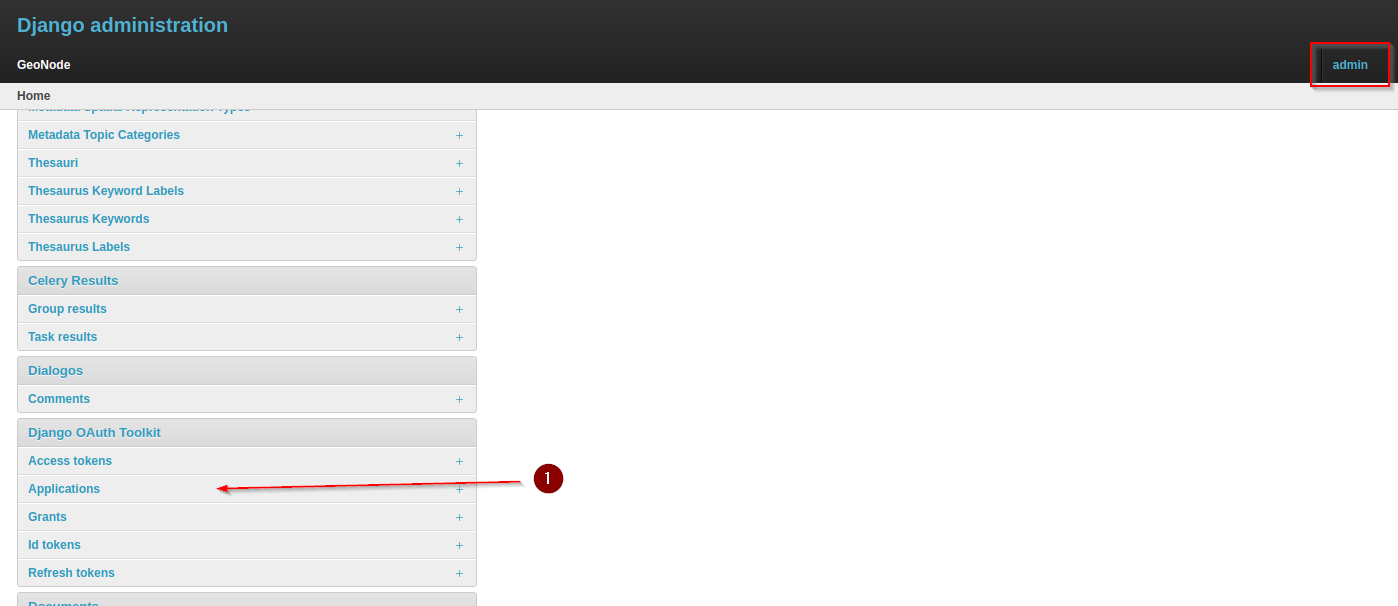
Edit the
GeoServerone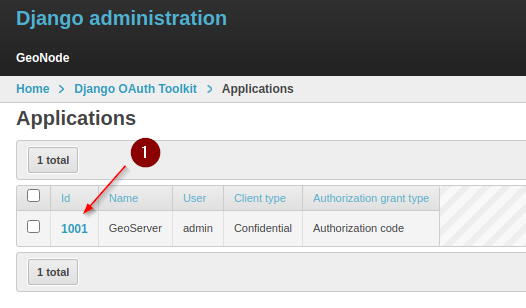
Add the following URL to the
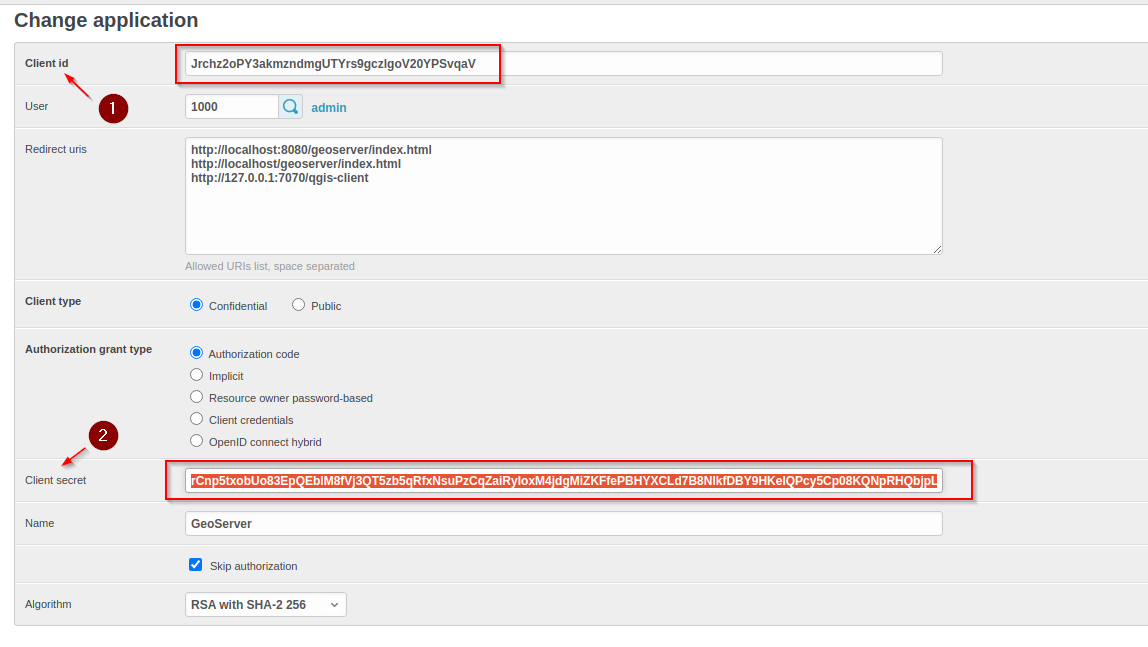
Redirect URIssection and take note of theClient IDandClient Secretkeys:Copy the Client ID / Client Secret
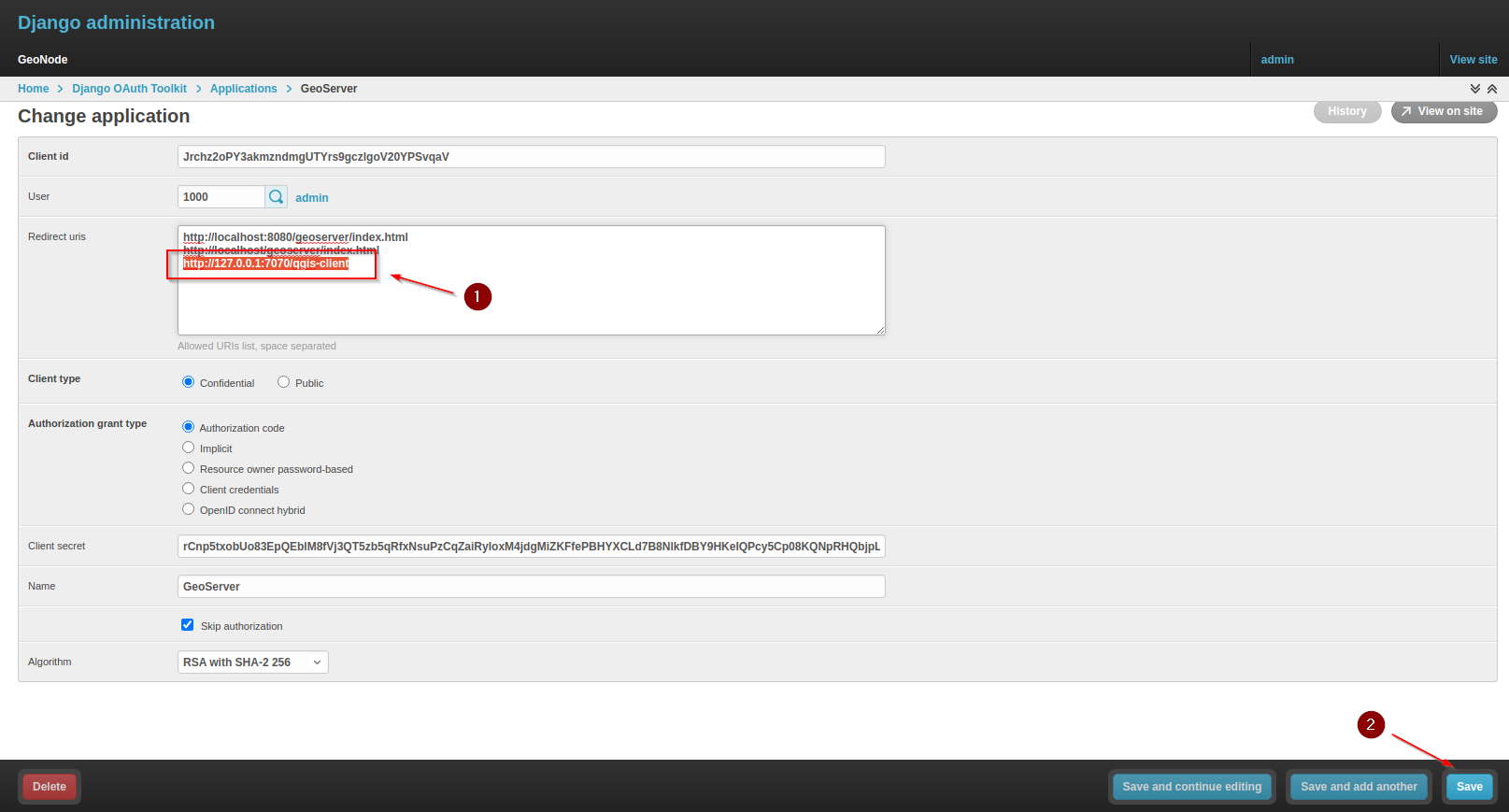
Add Redirect URIs and Save:
http://127.0.0.1:7070/qgis-client
Let’s add a
VECTORIALlayer accessible totest_user1to the client. Click onLayer > Add Layer > Add WFS Layer...
Add a new
OAuth2 Authenticationconfig and fill the fields as follows:Name: Provide any name you want, e.g.
GeoNode OAuth2Grant Flow:
Authorization CodeRequest URL:
http://localhost/o/authorize/(the/at the end is IMPORTANT!)Token URL:
http://localhost/o/token/(the/at the end is IMPORTANT!)Refresh token URL:
http://localhost/o/token/(the/at the end is IMPORTANT!)Client ID / Client Secret: The ones above
Scope:
openid writeToken session:
TrueAccess method:
HeaderToken header: empty (it is important you leave this parameter empty)
Save
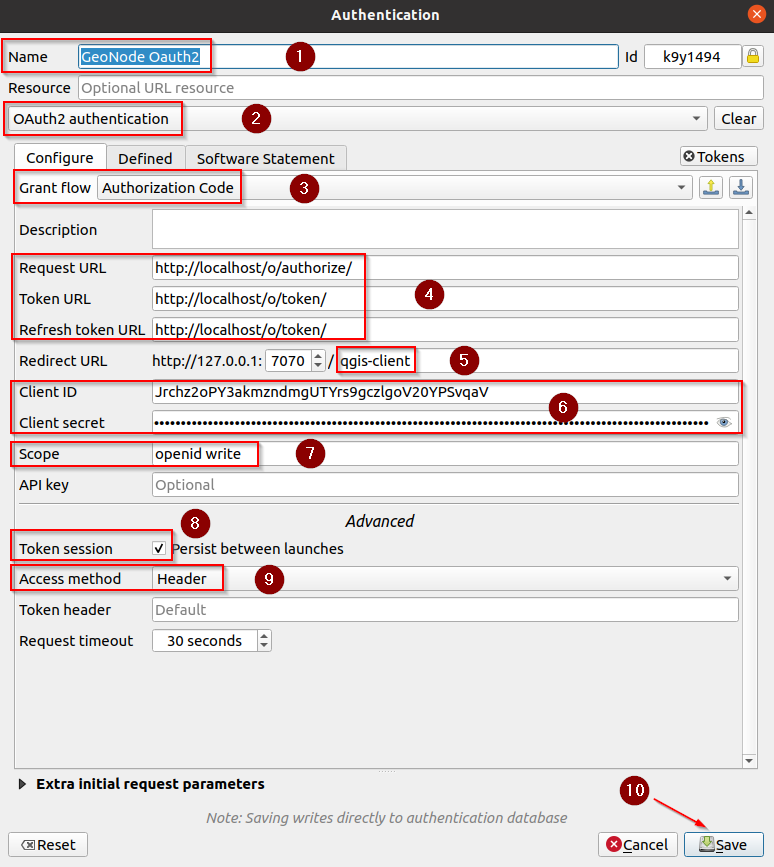
Make sure the new configuration is selected, and click on
Detectto verify that it works. Click onOKwhen finished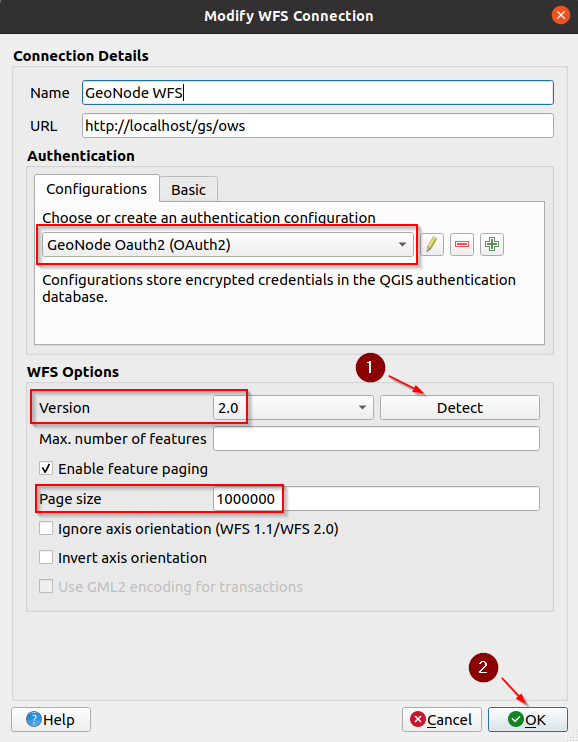
The client will automatically open a browser session. If you are not logged in, sign in with
admin(or whatever user you want).The window below means that the authentication process was successful. You can safely close it and go back to the client
Throubleshooting: if the QGIS client does not correctly redirect to the browser
Check that the
Default Applicationfor theWEBis set toFirefox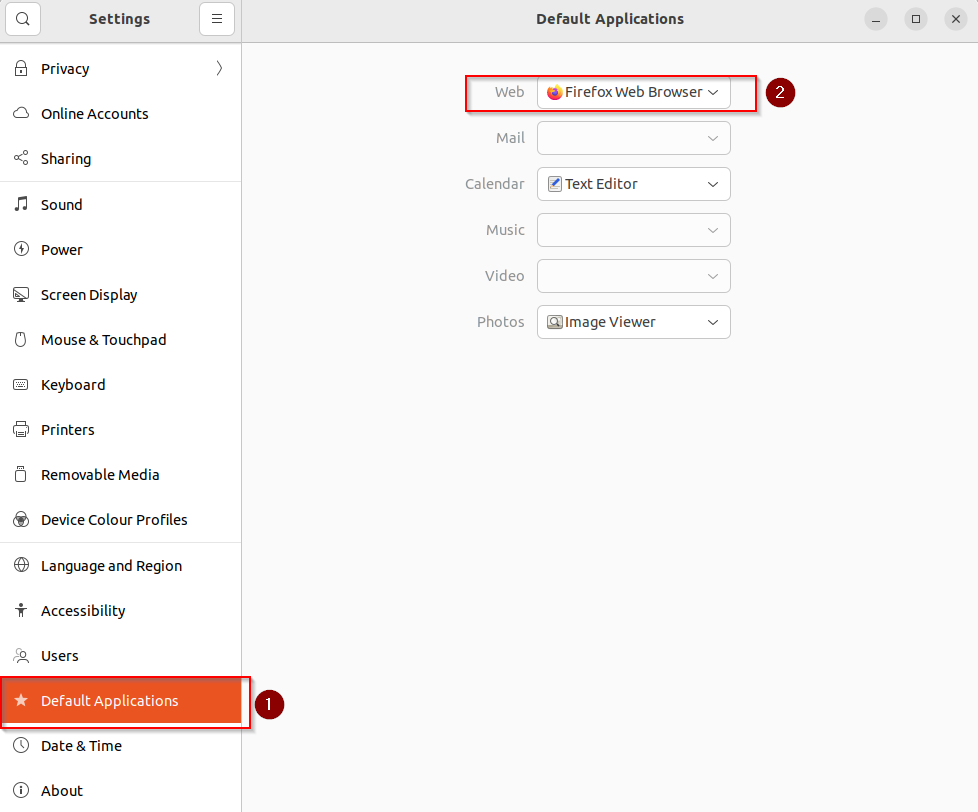
If this is not the case, open a
Terminalwindow and run the following command lines:sudo apt update sudo apt install firefox
Close the
Firefoxwindows and try again.
Throubleshooting: if the QGIS client returns a redirect uri error code
In the case you get an error like this
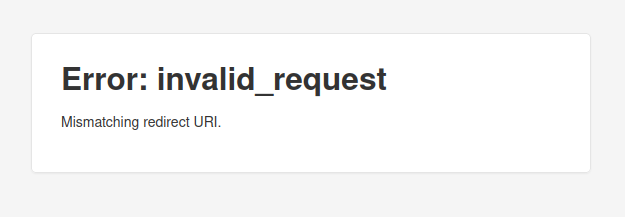
Check the
URLon the browser location bar and make sure theredirect_uriis set tohttp://127.0.0.1:7070/qgis-client; if not, change it manually and refresh!This should be also added to the GeoNode
Oauth2application.
Attach Layer to the Project
Once the connection has been configured and saved, whatever it is, go back to the
WFSpanel, select the connection you just created and click onConnect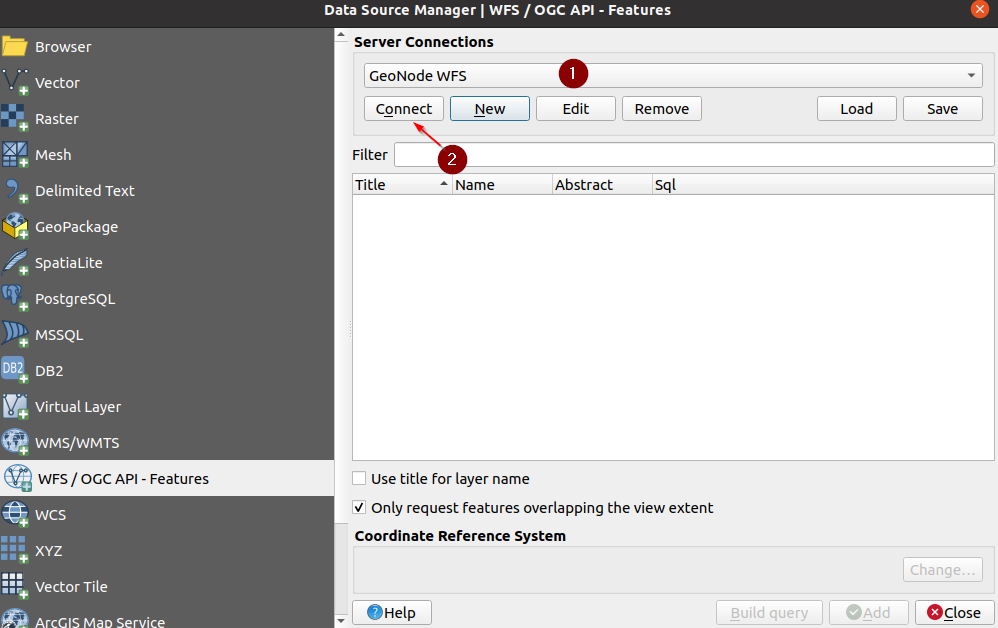
If everything goes well, you should be able to see the server offering. It will list all the layers the user has access to
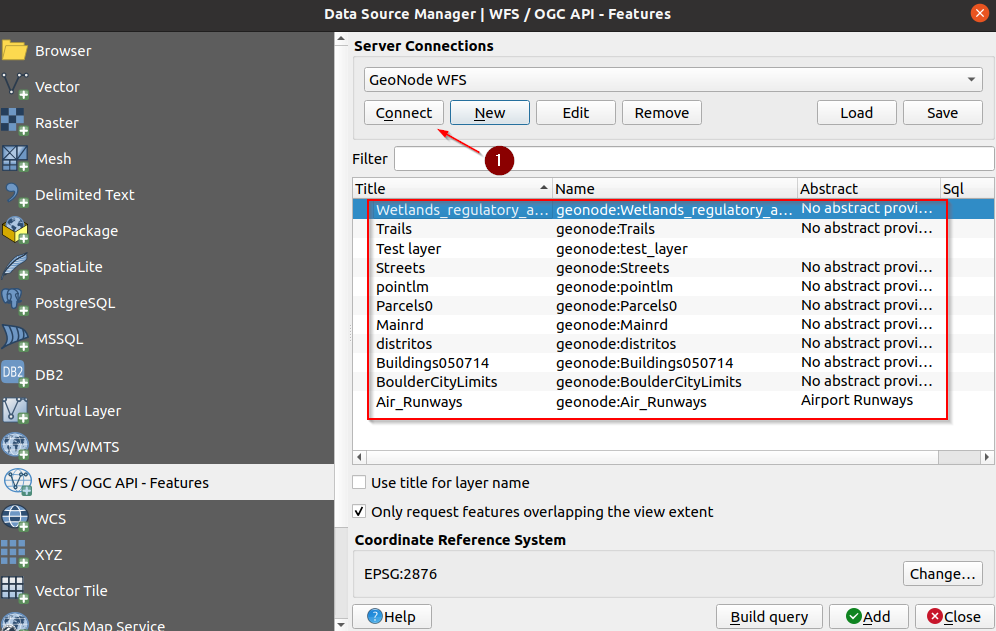
Select the
Test Layer, and click onAdd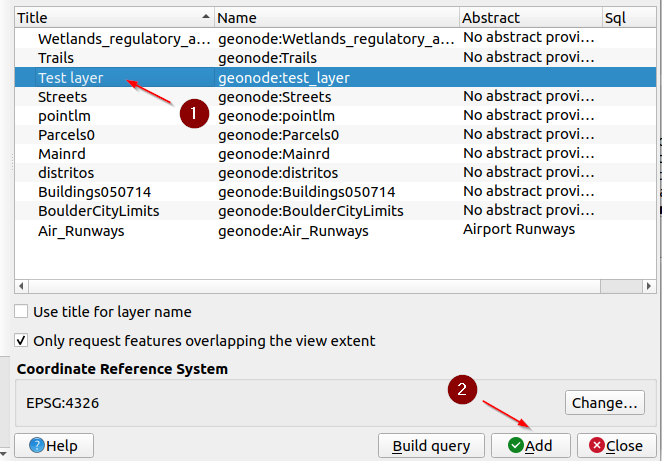
QGIS will create a new project with the layer already loaded and centered on the map
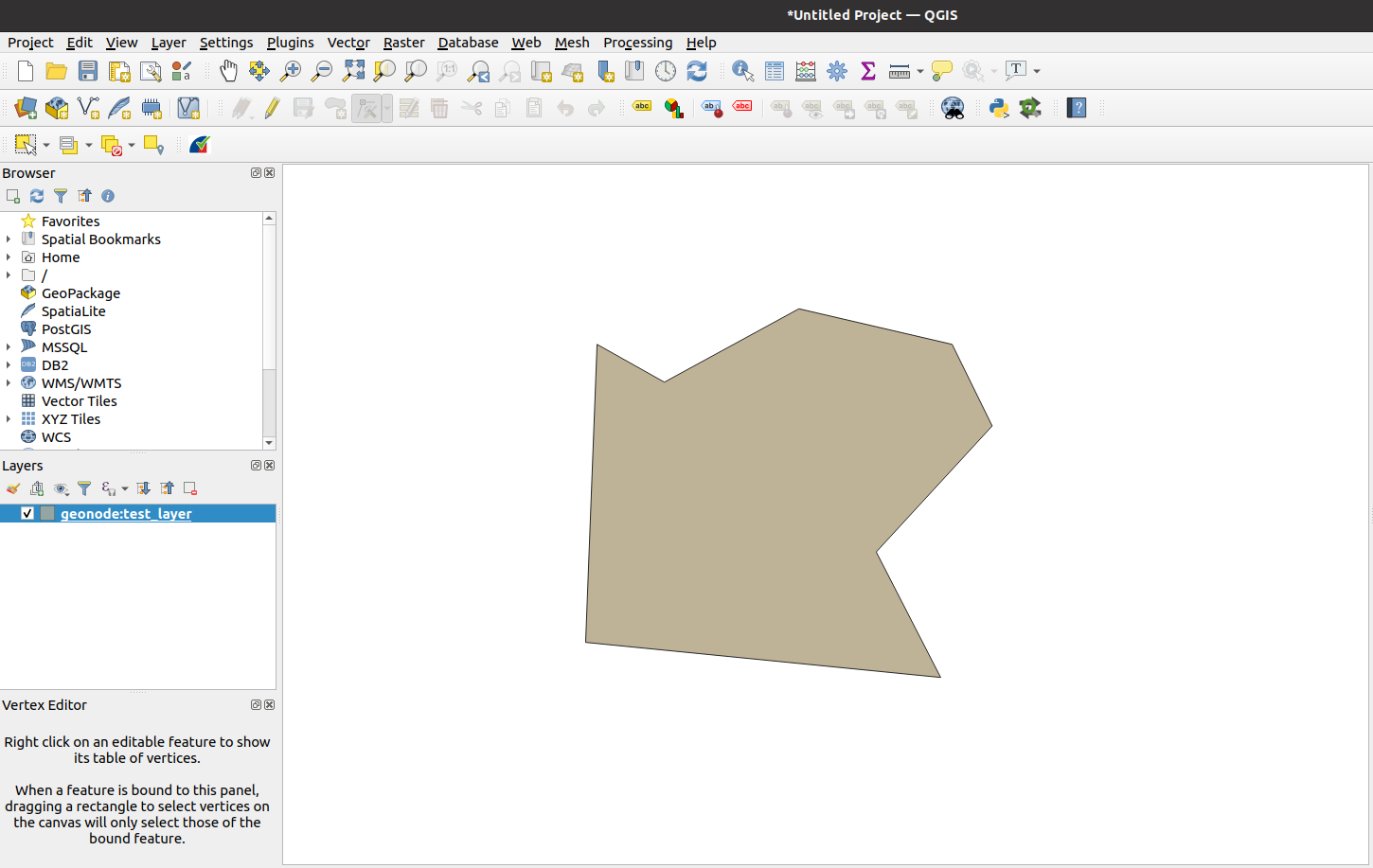
Editing Contents: Values
Enable
Editing Modeon QGIS, and click on theInfobutton
Click over the geometry to edit, and on the right-hand panel, expand and click on the link
Edit feature form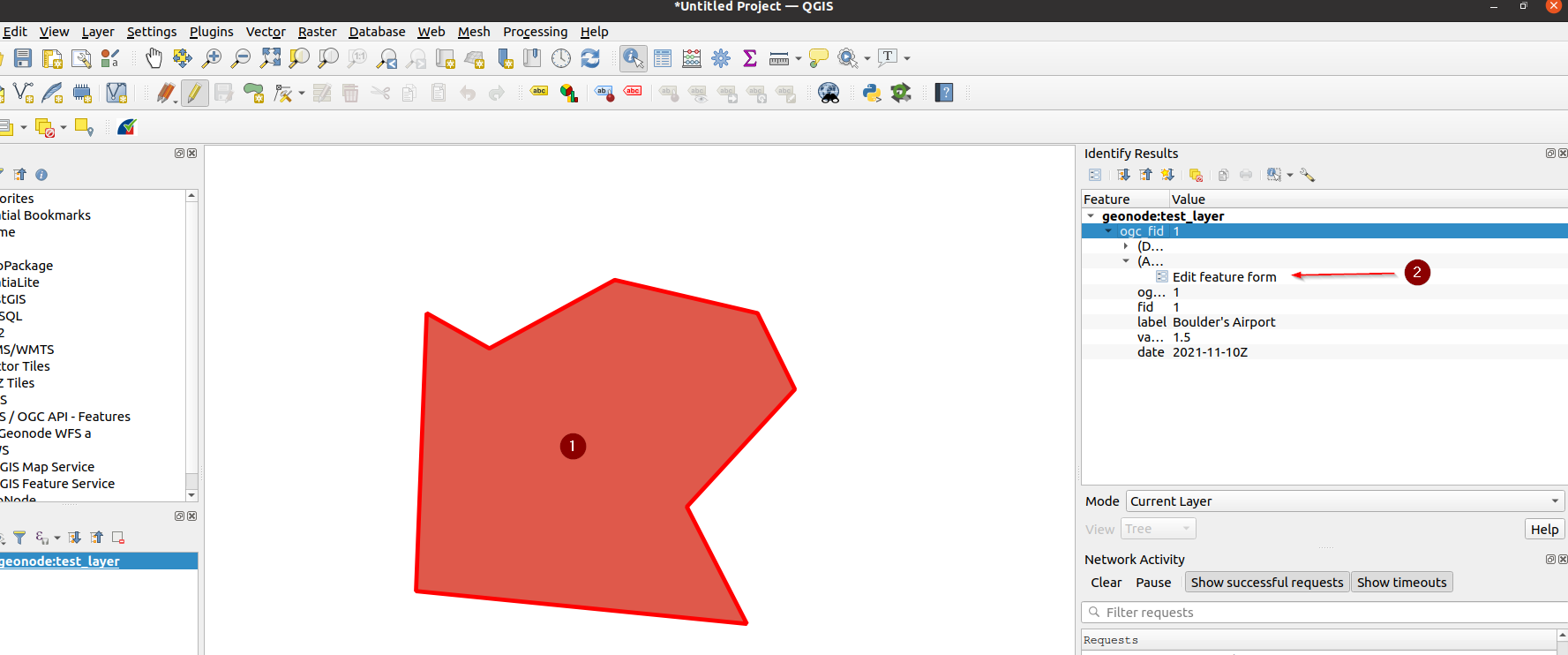
That will show a small form with the values, change a few of them, and click on the
OKbutton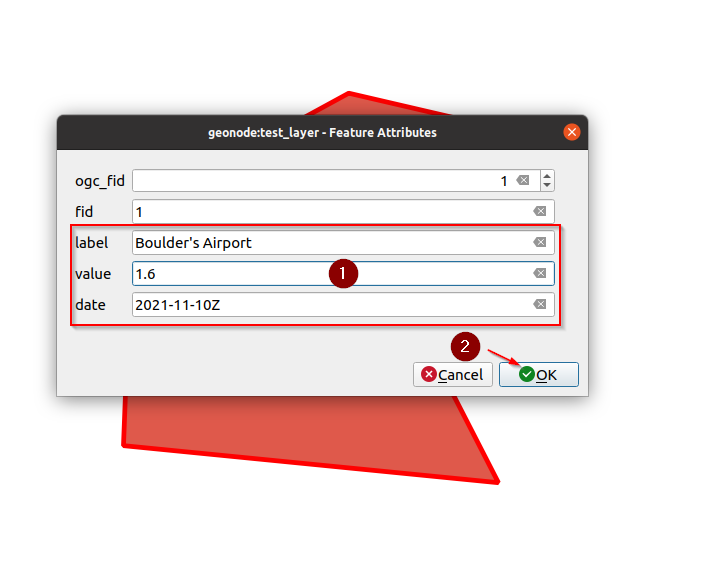
A small
floppy diskbutton will enable near the editing one meaning that there are some pending changes to be committed to the server. Click on it in order to persist the changes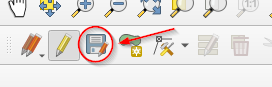
After a successful commit, the
floppy diskbutton will be disabled again
Editing Contents: Geometries
Enable
Editing Modeon QGIS and click on theInfobutton
Click on the
Vertex Tooland enable it. From now on, you will be able to modify a geometry’s vertices by moving over it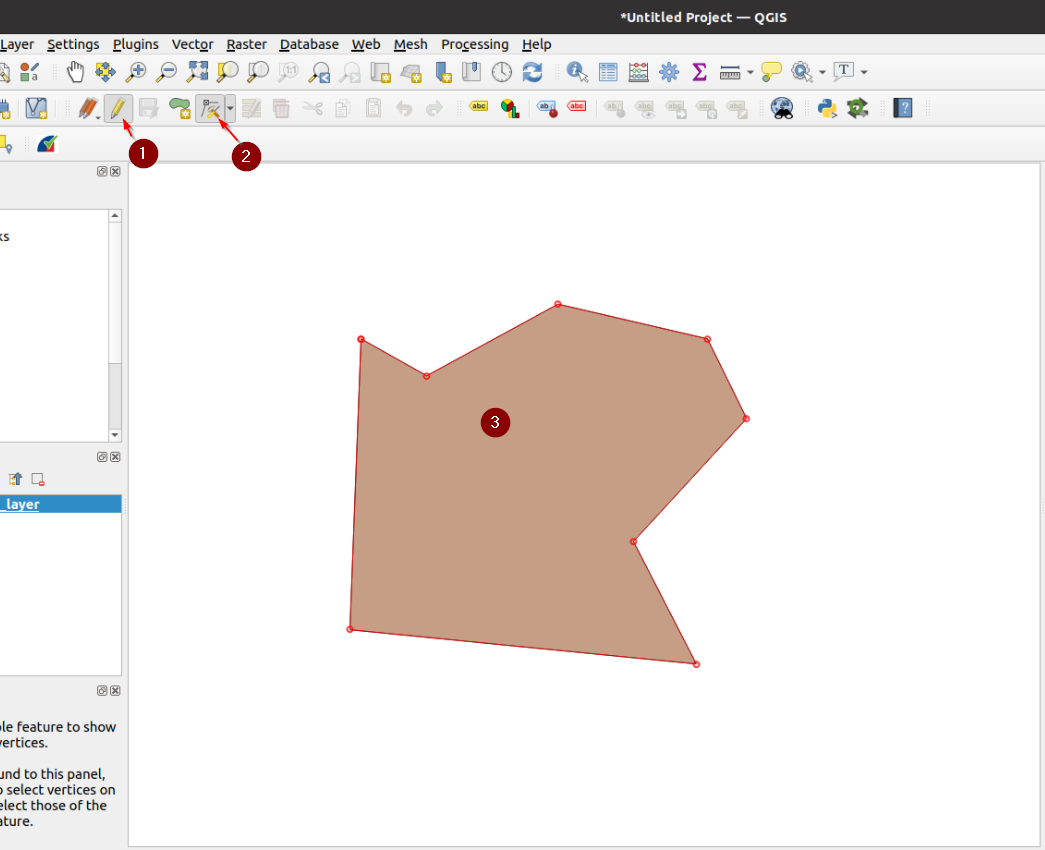
Once happy with the changes, save them as we have done previously with the values
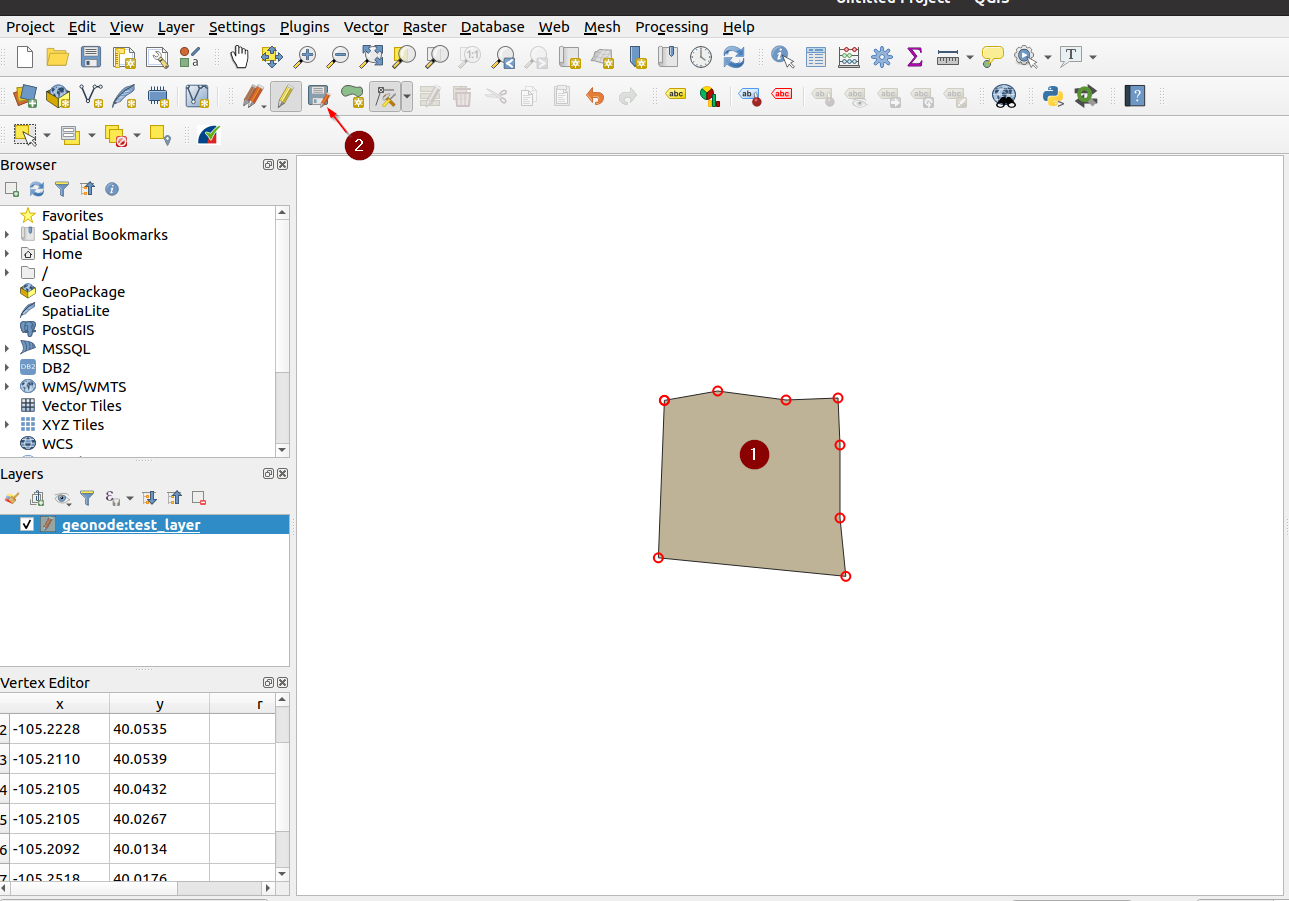
With this specific layer, you will most probably get an error on the bounding box extension. This is caused by the native projection of the layer, and QGIS not being able to correctly manage the
dateline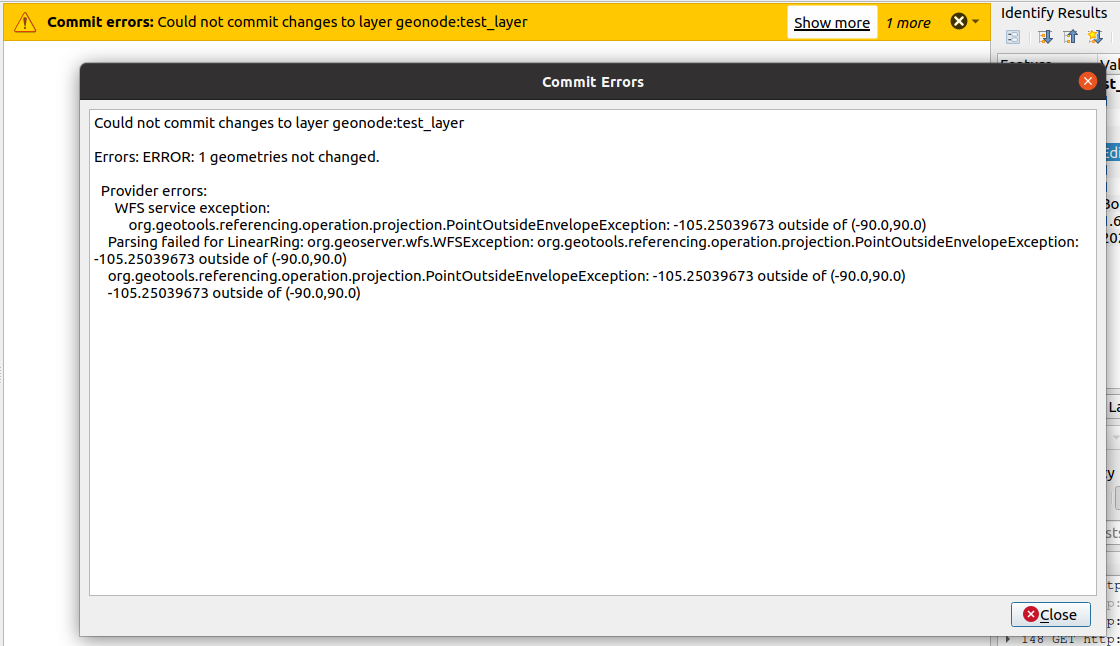
It is still possible to edit the layer from GeoNode directly. However, to fix this issue easily, we will convert the layer into a
Mercator Projectedone.
We will pass it through the database to perform such an operation. In the next section, we will see how to re-project and store a DB table in a layer and then push it back to GeoNode.