Add an app to a geonode project
In this section, we will show how to create and set up the skeleton of a custom app using the Django facilities.
The Geocollections app will show the resources and users, grouped by a GeoNode Profile, on a single page.
We will be able to assign arbitrary resources, and a profile and name to a Geocollection; the latter will also be used to build a dedicated URL.
Create the Django app
Django provides handy commands to create and manage apps. We already used
startprojectto create ourgeonode-projectinstance. Now we will usestartappto create anapp.workon my_geonode cd /opt/geonode-project/my_geonode/src ./manage_dev.sh startapp geocollections
This will create a folder named
geocollectionscontaining emptymodelsandviews.We need to add the new app to the
INSTALLED_APPSof our project.
Editmy_geonode/settings.pyand go toline 60:vim my_geonode/settings.pydiff --git a/my_geonode/settings.py b/my_geonode/settings.py index d9ac76a..786b29f 100644 --- a/my_geonode/settings.py +++ b/my_geonode/settings.py @@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ WSGI_APPLICATION = "{}.wsgi.application".format(PROJECT_NAME) LANGUAGE_CODE = os.getenv('LANGUAGE_CODE', "en") if PROJECT_NAME not in INSTALLED_APPS: - INSTALLED_APPS += (PROJECT_NAME, ) + INSTALLED_APPS += (PROJECT_NAME, 'geocollections', ) # Location of url mappings ROOT_URLCONF = os.getenv('ROOT_URLCONF', '{}.urls'.format(PROJECT_NAME))
Add custom models, views, and URLs
Add the new model (here’s the code)
vim geocollections/models.pyfrom django.db import models from geonode.base.models import ResourceBase from geonode.groups.models import GroupProfile class Geocollection(models.Model): """ A collection is a set of resources linked to a GeoNode group """ group = models.ForeignKey(GroupProfile, related_name='group_collections', on_delete=models.CASCADE) resources = models.ManyToManyField(ResourceBase, related_name='resource_collections') name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True) slug = models.SlugField(max_length=128, unique=True) def __str__(self): return self.name
At this point, we need Django to handle the changes in the DB.
Django, since version 1.8, provides an embedded migration mechanism.
We are going to use it to change the state of the DB.Create the migration files for the new models:
./manage_dev.sh makemigrationsOutput:
# the command above shows the migrations to be executed on the database Migrations for 'geocollections': geocollections/migrations/0001_initial.py - Create model Geocollection
Apply the migrations to the database:
./manage_dev.sh migrateOutput:
Operations to perform: Apply all migrations: account, actstream, admin, announcements, auth, avatar, base, br, contenttypes, dialogos, django_celery_beat, django_celery_results, documents, favorite, geoapp_geostories, geoapps, geocollections, geonode_client, geonode_themes, groups, guardian, invitations, layers, maps, mapstore2_adapter, monitoring, oauth2_provider, people, pinax_notifications, ratings, services, sessions, sites, socialaccount, taggit, tastypie, upload, user_messages Running migrations: Applying geocollections.0001_initial... OK
Add a django generic view to show the collection’s details
vim geocollections/views.pyfrom django.views.generic import DetailView from .models import Geocollection class GeocollectionDetail(DetailView): model = Geocollection
To access the view we just created, we will need some url mapping definitions.
The urls.py file contains a url mapping to our generic view
vim geocollections/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from .views import GeocollectionDetail
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^(?P<slug>[-\w]+)/$',
GeocollectionDetail.as_view(),
name='geocollection-detail'),
]
We also need to register the app URLs to the GeoNode project URLs.
Let’s modify themy_geonodeurls.pyfile adding the following mappings.vim my_geonode/urls.pydiff --git a/my_geonode/urls.py b/my_geonode/urls.py index 07b694f..bcf1cb7 100644 --- a/my_geonode/urls.py +++ b/my_geonode/urls.py @@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ from geonode.base import register_url_event urlpatterns += [ ## include your urls here - + url(r'^geocollections/', include('geocollections.urls')), ]
Create admin panel for geocollections models
We need a user interface to allow us to create geocollections.
Django makes this very easy, we just need to add them to the admin.py file as follows.
vim geocollections/admin.py
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Geocollection
class GeocollectionAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
prepopulated_fields = {"slug": ("name",)}
filter_horizontal = ('resources',)
admin.site.register(Geocollection, GeocollectionAdmin)
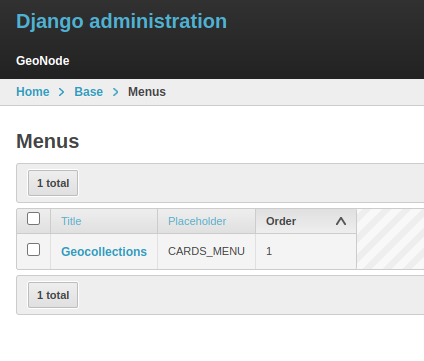
Browse http://localhost:8000/admin/ and search for the Geocollections tab:
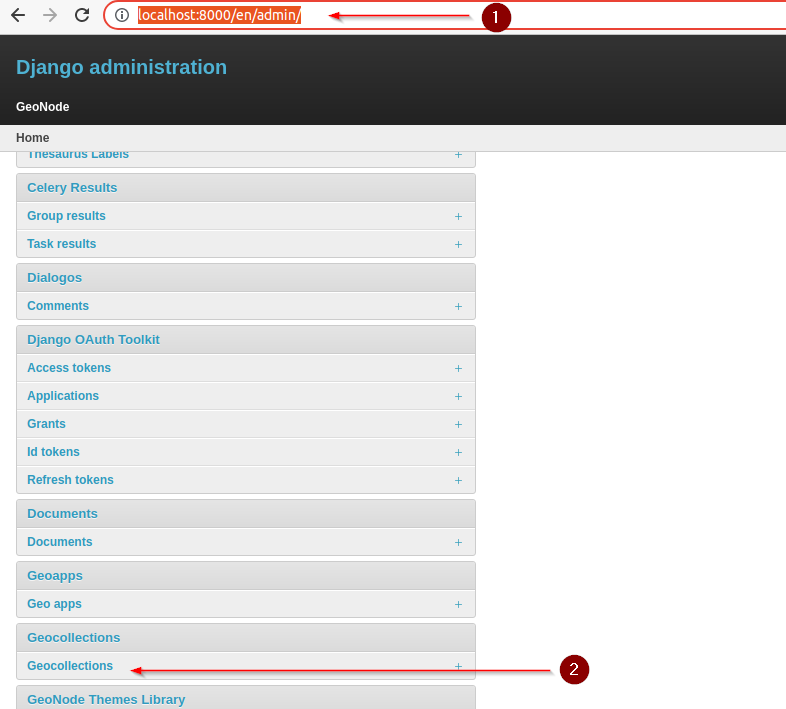
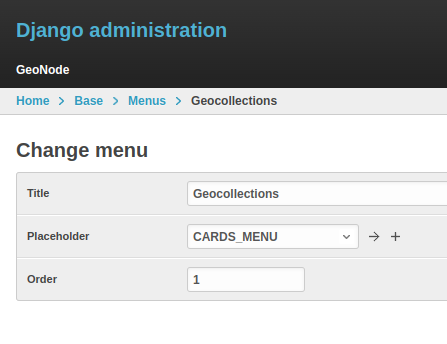
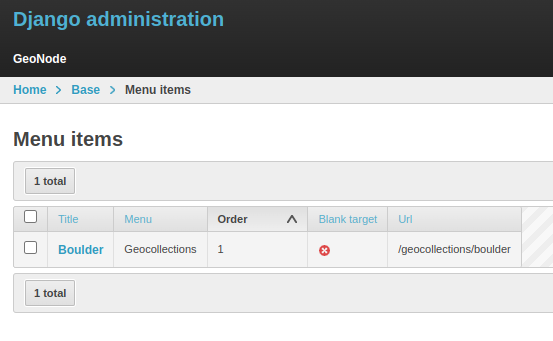
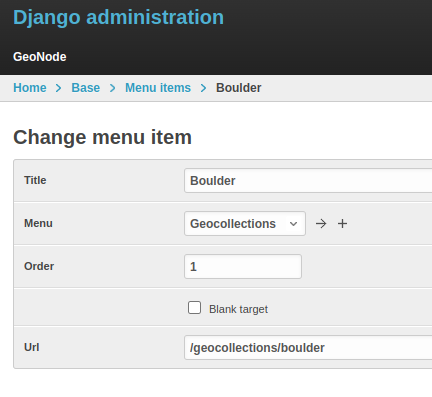
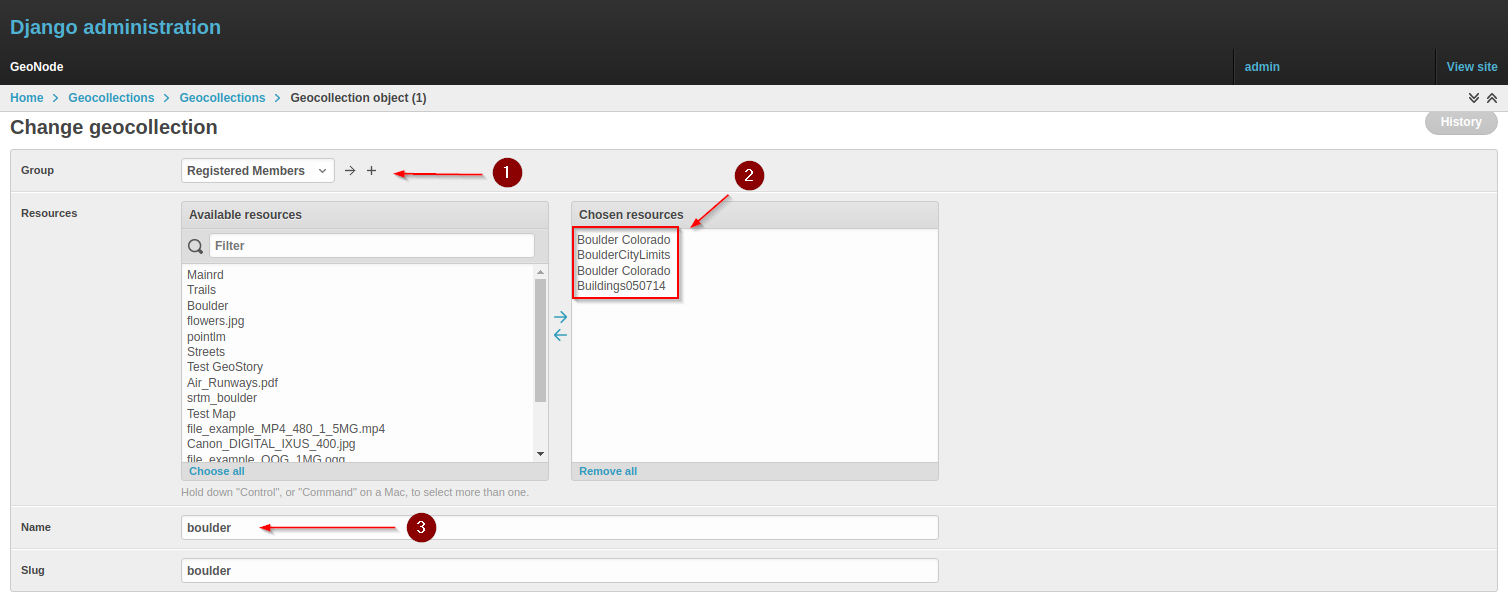
Create a new Geocollection named boulder and add some resources to it
Adding the Geocollections Details Template
The last thing we need to add to render the Geocollection details is the HTML template used by the Django view
vim my_geonode/settings.py
...
TEMPLATES[0]['DIRS'].insert(1, os.path.join('geocollections', "templates"))
...
mkdir -p geocollections/templates/geocollections/
vim geocollections/templates/geocollections/geocollection_detail.html
{% extends "page.html" %}
{% block container %}
<div class="geocollection-custom-page-container">
<p class="h2">Geocollection {{ object.name }}</p>
<p>Group: {{ object.group.title }}</p>
<p>Resources:</p>
<ul class="list-group">
{% for resource in object.resources.all %}
<li class="list-group-item bordertopbottom">
<div><a href="{{resource.detail_url}}" target="_blank">{{resource.title}}</a><div>
<div>{{resource.abstract|safe}}</div>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
{% endblock %}
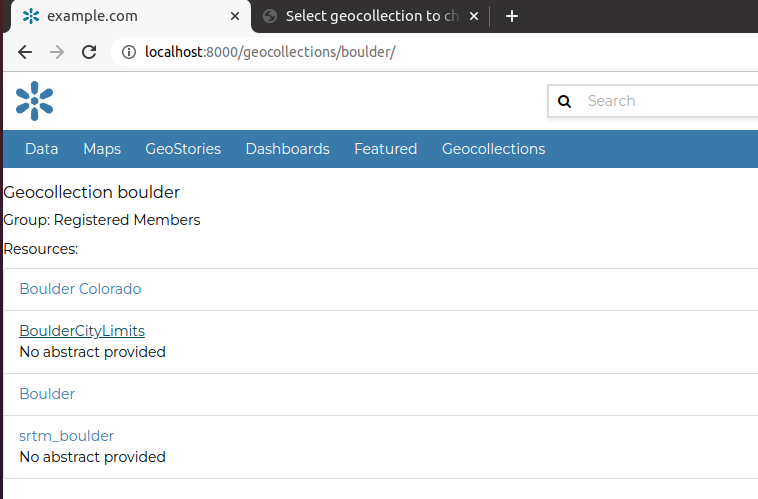
Now try visiting the geocollection we just created; go to http://localhost:8000/geocollections/boulder/
The URLs of the geocollection are in the form http://localhost:8000/geocollections/<the-name-of-the-created-geocollection>
Permissions
The permissions in GeoNode are managed by django-guardian, a python library allowing the setting object level permissions (Django has table level authorization).
The first thing to do is to add the permissions object to the database. We can do this by adding the following Meta class to our Geocollection model, guardian will take care of creating the objects for us.
vim geocollections/models.py
--- geocollections/models_00.py 2021-10-28 17:35:06.499794009 +0200
+++ geocollections/models_01.py 2021-10-28 17:36:12.791491477 +0200
@@ -15,3 +15,8 @@
def __str__(self):
return self.name
+
+ class Meta:
+ permissions = (
+ ('access_geocollection', 'Can view geocollection'),
+ )
Run the makemigrations and migrate management commands to install them
./manage_dev.sh makemigrations
./manage_dev.sh migrate
Please note that it is not possible to define any permissions with prefixes like view_, add_, delete_, or something, because those have been natively introduced by Django since version 2.1.
Permission logic methods
Let’s add a few methods to the Geocollection models and views to be able to manage the permissions
vim geocollections/models.py
Here’s the new model class.
(We are not showing the diff here because it would be too long.)
Default permissions
Let’s test the set_default_permissions method:
./manage_dev.sh shell
Python 3.10 (default, Jun 2 2021, 10:49:15)
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 7.24.1 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: from geocollections.models import Geocollection
In [2]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').set_default_permissions()
In [3]: quit()
Permissions Setter on perm_spec
A perm_spec in GeoNode is an object that declares the set of permissions to assign to users, groups, or both.
Please note that in this context, a group is a Django authority group that is related to a GeoNode GroupProfile through its slug.
A sample perm_spec is something like this (you may want to use this code later on in the python shell):
perm_spec = {
"users": {
"AnonymousUser": [],
"test_user1": ["access_geocollection"],
"test_user2": [],
},
"groups": {
"registered-members": ["access_geocollection"]
}
}
Let’s test the set_permissions method:
./manage_dev.sh shell
Python 3.10.10 (default, Jun 2 2021, 10:49:15)
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 7.24.1 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: from geocollections.models import Geocollection
In [2]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').set_default_permissions()
In [3]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').get_all_level_info()
Out[3]:
{'users': {},
'groups': {<Group: anonymous>: ['access_geocollection'],
<Group: registered-members>: ['access_geocollection']}}
In [4]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').remove_object_permissions()
In [5]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').get_all_level_info()
Out[5]: {'users': {}, 'groups': {}}
# *** PASTE AND COPY FROM THE PREVIOUS CLEAN JSON CODE
In [6]: perm_spec = {
...: "users": {
...: "AnonymousUser": [],
...: "test_user1": ["access_geocollection"],
...: "test_user2": [],
...: },
...: "groups": {
...: "registered-members": ["access_geocollection"]
...: }
...: }
# *** MAKE SURE YOU HAVE THE USERS test_user1 AND test_user2
In [7]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').set_permissions(perm_spec)
assign_perm 'AnonymousUser' -> []
assign_perm 'test_user1' -> ['access_geocollection']
assign_perm 'test_user2' -> []
In [8]: Geocollection.objects.get(slug='boulder').get_all_level_info()
Out[8]:
{'users': {<Profile: test_user1>: ['access_geocollection']},
'groups': {<Group: registered-members>: ['access_geocollection']}}
In [9]: quit()
Permissions Views and Urls
Let’s use the access_geocollection permissions to control access to the views.
We will also define a specific view allowing us to check/set the geocollection permissions.
vim geocollections/views.py
--- geocollections/views_00.py 2021-10-28 19:49:21.335072043 +0200
+++ geocollections/views_01.py 2021-10-28 19:47:48.067500735 +0200
@@ -1,7 +1,32 @@
+import json
+import logging
+import traceback
+
+from django.shortcuts import render
+from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.views.generic import DetailView
+from django.core.exceptions import PermissionDenied
+from django.contrib.auth.mixins import PermissionRequiredMixin
from .models import Geocollection
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
+
-class GeocollectionDetail(DetailView):
+class GeocollectionDetail(PermissionRequiredMixin, DetailView):
model = Geocollection
+
+ def has_permission(self):
+ return self.request.user.has_perm('access_geocollection', self.get_object())
+
+def geocollection_permissions(request, collection_slug):
+ geocollection = Geocollection.objects.get(slug=collection_slug)
+ user = request.user
+
+ if user.has_perm('access_geocollection', geocollection):
+ return HttpResponse(
+ (f'You have the permission to access the geocollection "{collection_slug}". '
+ 'Please customize a template for this view'),
+ content_type='text/plain')
+ else:
+ raise PermissionDenied
Now bind a new urlpattern to access the geocollection_permissions view.
vim geocollections/urls.py
--- geocollections/urls.py.org 2021-09-13 23:43:40.534056180 +0100
+++ geocollections/urls.py 2021-09-13 23:46:45.172949596 +0100
@@ -1,9 +1,12 @@
from django.conf.urls import url
-from .views import GeocollectionDetail
+from .views import GeocollectionDetail, geocollection_permissions
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^(?P<slug>[-\w]+)/$',
GeocollectionDetail.as_view(),
name='geocollection-detail'),
+ url(r'^permissions/(?P<collection_slug>[-\w]+)/$',
+ geocollection_permissions,
+ name='geocollection_permissions')
]
Trying to access the views as an admin, we will be able to get both the details and check the permissions.
admin
http://localhost:8000/geocollections/boulder/
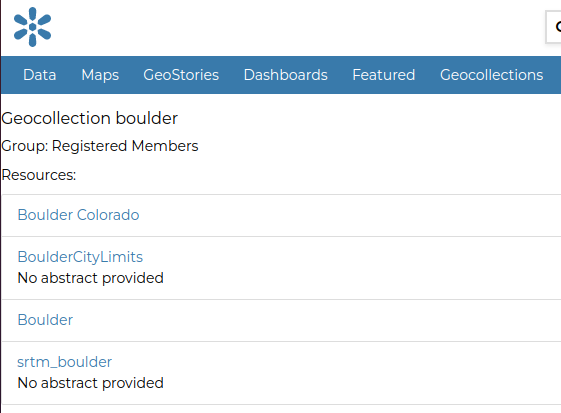
http://localhost:8000/geocollections/permissions/boulder/
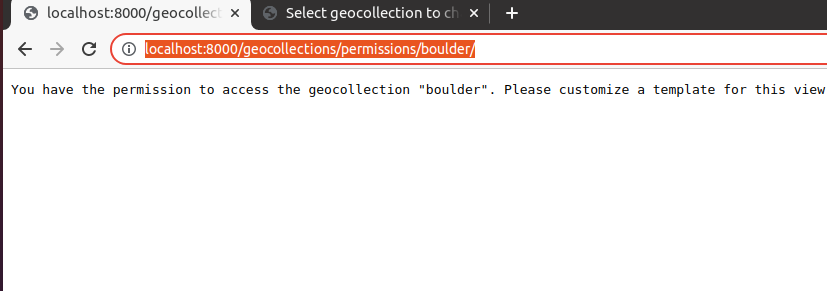
anonymous
Logout
http://localhost:8000/geocollections/boulder/
http://localhost:8000/geocollections/permissions/boulder/
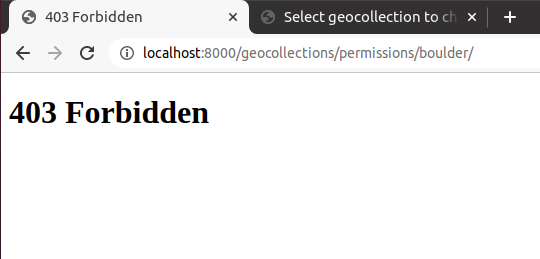
Permissions Set View Template
Let’s modify the geocollection_permissions view in order to return a FORM that allows a user to set the perm_spec from the browser
vim geocollections/views.py
--- geocollections/views.py.org 2021-09-13 23:36:59.410056180 +0100
+++ geocollections/views.py 2021-09-14 01:15:30.513828438 +0100
@@ -1,6 +1,56 @@
+import json
+import logging
+import traceback
+
+from django.shortcuts import render
+from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.views.generic import DetailView
+from django.core.exceptions import PermissionDenied
+from django.contrib.auth.mixins import PermissionRequiredMixin
from .models import Geocollection
-class GeocollectionDetail(DetailView):
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
+
+
+class GeocollectionDetail(PermissionRequiredMixin, DetailView):
model = Geocollection
+
+ def has_permission(self):
+ return self.request.user.has_perm('access_geocollection', self.get_object())
+
+
+def geocollection_permissions(request, collection_slug):
+
+ geocollection = Geocollection.objects.get(name=collection_slug)
+ user = request.user
+
+ if not user.has_perm('access_geocollection', geocollection):
+ raise PermissionDenied
+
+ if request.method == 'GET':
+ return render(request, 'geocollections/geocollection_permissions.html', context={'object': geocollection})
+
+ elif request.method == 'POST':
+ success = True
+ message = "Permissions successfully updated!"
+ try:
+ perm_spec = json.loads(request.POST.get('perm_spec'))
+ logger.info(f" ---- setting perm_sepc: {perm_spec}")
+ geocollection.set_permissions(perm_spec)
+
+ return HttpResponse(
+ json.dumps({'success': success, 'message': message}),
+ status=200,
+ content_type='text/plain'
+ )
+ except Exception as e:
+ traceback.print_exc()
+ logger.exception(e)
+ success = False
+ message = f"Error updating permissions :(... error: {e}"
+ return HttpResponse(
+ json.dumps({'success': success, 'message': message}),
+ status=500,
+ content_type='text/plain'
+ )
Now, let’s define the geocollections/geocollection_permissions.html template to render and manage the perm_spec request.
vim geocollections/templates/geocollections/geocollection_permissions.html
{% extends "page.html" %}
{% block container %}
<h1>Geocollection: <b>{{ object.name }}</b></h1>
<p>You have the permission to access the Geocollection: {{ object.name }}</p>
<p>Geocollection Permissions:</p>
<form action="/geocollections/permissions/{{ object.slug }}/" method="POST" name="geocollections_perm_spec_form">
{% csrf_token %}
<label for="perm_spec">Perm Spec: </label><br>
<textarea id="perm_spec" name="perm_spec" rows=4 cols="50">{{ object.get_all_level_info }}</textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Change Permissions">
</form>
{% endblock %}
{% block extra_script %}
{{ block.super }}
{% endblock extra_script %}
vim geocollections/templates/geocollections/geocollection_detail.html
{% extends "page.html" %}
{% block container %}
<div class="geocollection-custom-page-container">
<p class="h1">Geocollection: <strong>{{ object.name }}</strong></p>
{% if user.is_superuser %}
<a href="/geocollections/permissions/{{ object.slug }}">Edit Permissions</a>
{% endif %}
<p>Group: <i>{{ object.group.title }}</i></p>
<p>Resources:</p>
<ul class="list-group">
{% for resource in object.resources.all %}
<li class="list-group-item bordertopbottom">
<div><a href="{{ resource.detail_url }}" target="_blank">{{ resource.title }}</a><div>
<div>{{ resource.custom_md|safe }}</div>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
{% endblock %}
Let’s test it. Navigate to
http://localhost:8000/geocollections/permissions/boulder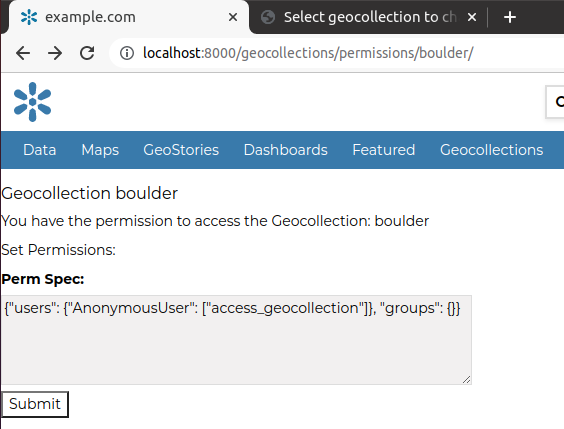
Update the
perm_specand click onSubmit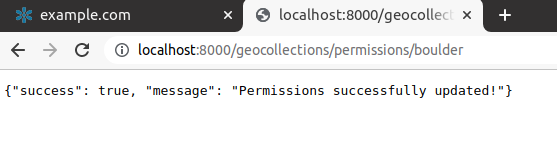
Let’s check if the
perm_spechas changed on the backend
./manage_dev.sh shell
Python 3.10 (default, Jun 2 2021, 10:49:15)
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 7.24.1 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: from geocollections.models import Geocollection
In [2]: Geocollection.objects.get(name='boulder').get_all_level_info()
Out[2]:
{'users': {<Profile: AnonymousUser>: ['access_geocollection']},
'groups': {<Group: anonymous>: ['access_geocollection']}}
In [3]: quit()
Adding APIs to Geocollection App
In this section, we will implement a very simple instance of GeoNode APIs for our Geocollection app, along with some security integration.
Currently, GeoNode provides two types of API endpoints that are usually identified as API v1, provided through Django Tastypie, and API v2, which is provided by Django Rest Framework.
WARNING GeoNode 4.0 still provides support for the API v1. This is deprecated and will be dropped in future versions.
API v1 - Tastypie
Let’s create the
api.pyfile first
vim geocollections/api.py
import json
from tastypie.resources import ModelResource
from tastypie import fields
from tastypie.constants import ALL_WITH_RELATIONS, ALL
from geonode.api.api import ProfileResource, GroupResource
from geonode.api.resourcebase_api import ResourceBaseResource
from .models import Geocollection
class GeocollectionResource(ModelResource):
users = fields.ToManyField(ProfileResource, attribute=lambda bundle: bundle.obj.group.group.user_set.all(), full=True)
group = fields.ToOneField(GroupResource, 'group__group', full=True)
resources = fields.ToManyField(ResourceBaseResource, 'resources', full=True)
class Meta:
queryset = Geocollection.objects.all().order_by('-group')
ordering = ['group']
allowed_methods = ['get']
resource_name = 'geocollections'
filtering = {
'group': ALL_WITH_RELATIONS,
'id': ALL
}
API authorization
vim geocollections/api.py
--- geocollections/api.py.org 2021-09-14 11:02:11.106936710 +0100
+++ geocollections/api.py 2021-09-14 11:02:14.948856713 +0100
@@ -2,6 +2,9 @@
from tastypie.resources import ModelResource
from tastypie import fields
from tastypie.constants import ALL_WITH_RELATIONS, ALL
+from tastypie.authorization import DjangoAuthorization
+
+from guardian.shortcuts import get_objects_for_user
from geonode.api.api import ProfileResource, GroupResource
from geonode.api.resourcebase_api import ResourceBaseResource
@@ -9,6 +12,21 @@
from .models import Geocollection
+class GeocollectionAuth(DjangoAuthorization):
+
+ def read_list(self, object_list, bundle):
+ permitted_ids = get_objects_for_user(
+ bundle.request.user,
+ 'geocollections.access_geocollection').values('id')
+
+ return object_list.filter(id__in=permitted_ids)
+
+ def read_detail(self, object_list, bundle):
+ return bundle.request.user.has_perm(
+ 'access_geocollection',
+ bundle.obj)
+
+
class GeocollectionResource(ModelResource):
users = fields.ToManyField(ProfileResource, attribute=lambda bundle: bundle.obj.group.group.user_set.all(), full=True)
@@ -16,6 +34,7 @@
resources = fields.ToManyField(ResourceBaseResource, 'resources', full=True)
class Meta:
+ authorization = GeocollectionAuth()
queryset = Geocollection.objects.all().order_by('-group')
ordering = ['group']
allowed_methods = ['get']
API urls
vim my_geonode/urls.py
--- my_geonode/urls.py.org 2021-09-14 11:05:03.377028744 +0100
+++ my_geonode/urls.py 2021-09-14 11:05:54.934794761 +0100
@@ -24,8 +24,15 @@
from geonode.urls import urlpatterns
from geonode.base import register_url_event
+from geonode.api.urls import api
+
+from geocollections.api import GeocollectionResource
+
+api.register(GeocollectionResource())
+
urlpatterns += [
## include your urls here
+ url(r'', include(api.urls)),
url(r'^geocollections/', include('geocollections.urls')),
]
Let’s test them. As
adminnavigate tohttp://localhost:8000/api/geocollections/This is the result you should get.
To get the single object, as
adminnavigate tohttp://localhost:8000/api/geocollections/1:This is the result you should get.
As
anonymousnavigate tohttp://localhost:8000/api/geocollections/{ "meta": { "limit": 1000, "next": null, "offset": 0, "previous": null, "total_count": 0 }, "objects": [] }
API v2 - REST
API
ViewSet
vim geocollections/views.py
--- geocollections/views.py.org_2 2021-09-14 13:41:23.290625216 +0100
+++ geocollections/views.py 2021-09-14 13:46:01.578625216 +0100
@@ -8,7 +8,18 @@
from django.core.exceptions import PermissionDenied
from django.contrib.auth.mixins import PermissionRequiredMixin
+from dynamic_rest.viewsets import DynamicModelViewSet
+from dynamic_rest.filters import DynamicFilterBackend, DynamicSortingFilter
+
+from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly
+from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication
+from oauth2_provider.contrib.rest_framework import OAuth2Authentication
+
+from geonode.base.api.pagination import GeoNodeApiPagination
+
from .models import Geocollection
+from .serializers import GeocollectionSerializer
+from .permissions import GeocollectionPermissionsFilter
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@@ -54,3 +65,19 @@
status=500,
content_type='text/plain'
)
+
+
+class GeocollectionViewSet(DynamicModelViewSet):
+ """
+ API endpoint that allows geocollections to be viewed or edited.
+ """
+ authentication_classes = [SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication, OAuth2Authentication]
+ permission_classes = [IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly, ]
+ filter_backends = [
+ DynamicFilterBackend, DynamicSortingFilter,
+ GeocollectionPermissionsFilter
+ ]
+ queryset = Geocollection.objects.all()
+ serializer_class = GeocollectionSerializer
+ pagination_class = GeoNodeApiPagination
API
Permissions
vim geocollections/permissions.py
Here’s the new permissions file
from django.conf import settings
from rest_framework.filters import BaseFilterBackend
class GeocollectionPermissionsFilter(BaseFilterBackend):
"""
A filter backend that limits results to those where the requesting user
has read object-level permissions.
"""
shortcut_kwargs = {
'accept_global_perms': True,
}
def filter_queryset(self, request, queryset, view):
# We want to defer this import until runtime, rather than import-time.
# See https://github.com/encode/django-rest-framework/issues/4608
# (Also see #1624 for why we need to make this import explicitly)
from guardian.shortcuts import get_objects_for_user
user = request.user
obj_with_perms = get_objects_for_user(
user,
'geocollections.access_geocollection',
**self.shortcut_kwargs
)
return queryset.filter(id__in=obj_with_perms.values('id'))
API
Serializer
vim geocollections/serializers.py
Here’s the new serializers file
from dynamic_rest.serializers import DynamicModelSerializer
from .models import Geocollection
class GeocollectionSerializer(DynamicModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Geocollection
name = 'geocollection'
fields = (
'pk', 'name', 'group', 'resources'
)
API urls
vim my_geonode/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import include, url
from geonode.urls import urlpatterns
from geonode.api.urls import api
from geonode.api.urls import router
from geocollections.api import GeocollectionResource
from geocollections.views import GeocollectionViewSet
api.register(GeocollectionResource())
router.register(r'geocollections', GeocollectionViewSet, 'geocollections')
# You can register your own urlpatterns here
urlpatterns += [
url(r'', include(api.urls)),
url(r'^api/v2/', include(router.urls)),
url(r'^geocollections/', include('geocollections.urls')),
]
Let’s test them. As
adminnavigate tohttp://localhost:8000/api/v2/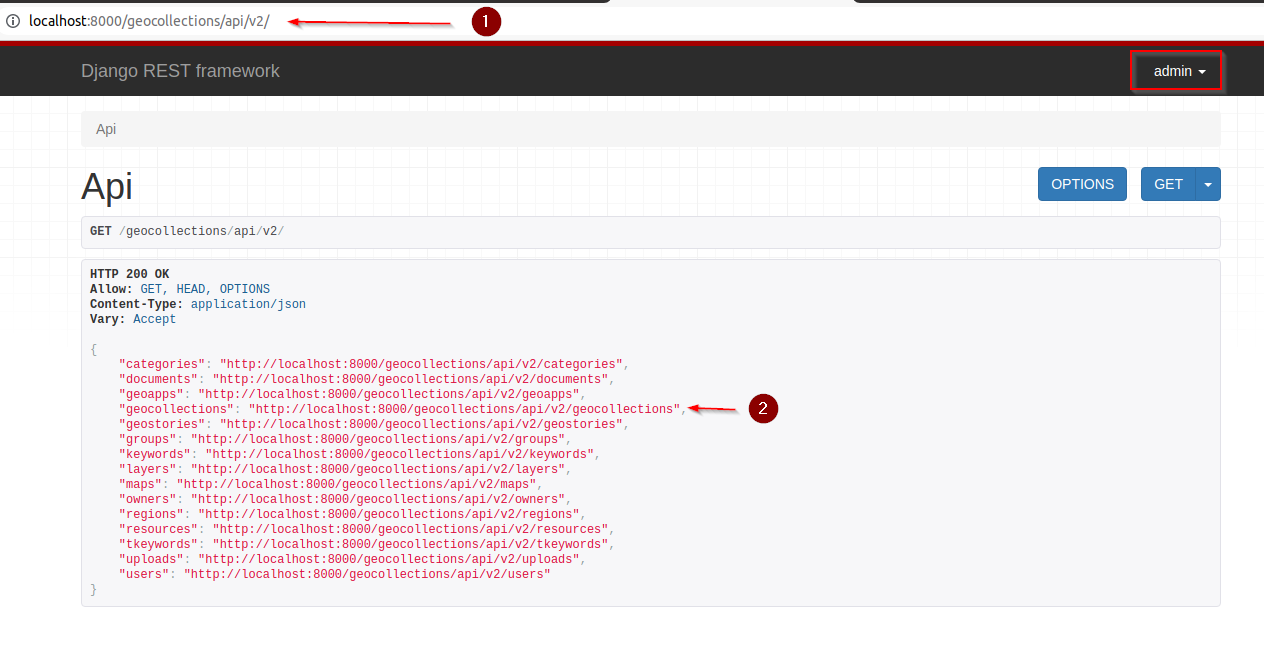
As
adminnavigate tohttp://localhost:8000/api/v2/geocollections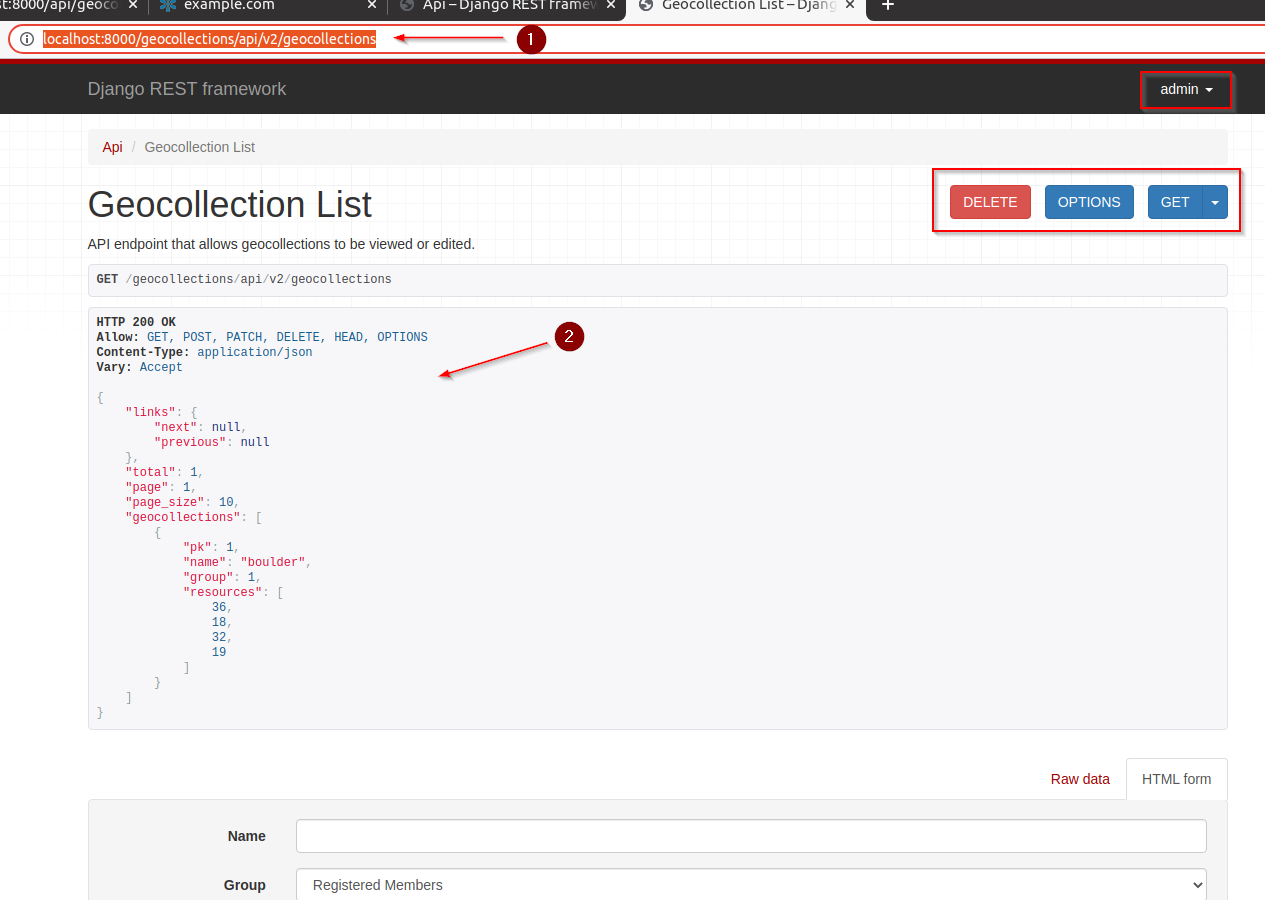
Note that through the
rest-frameworkit is also possible to executeCRUDoperationsTry some filtering;
http://localhost:8000/api/v2/geocollections?filter{name.contains}=boulAlso, try to
log outto see if thepermissionswork as expected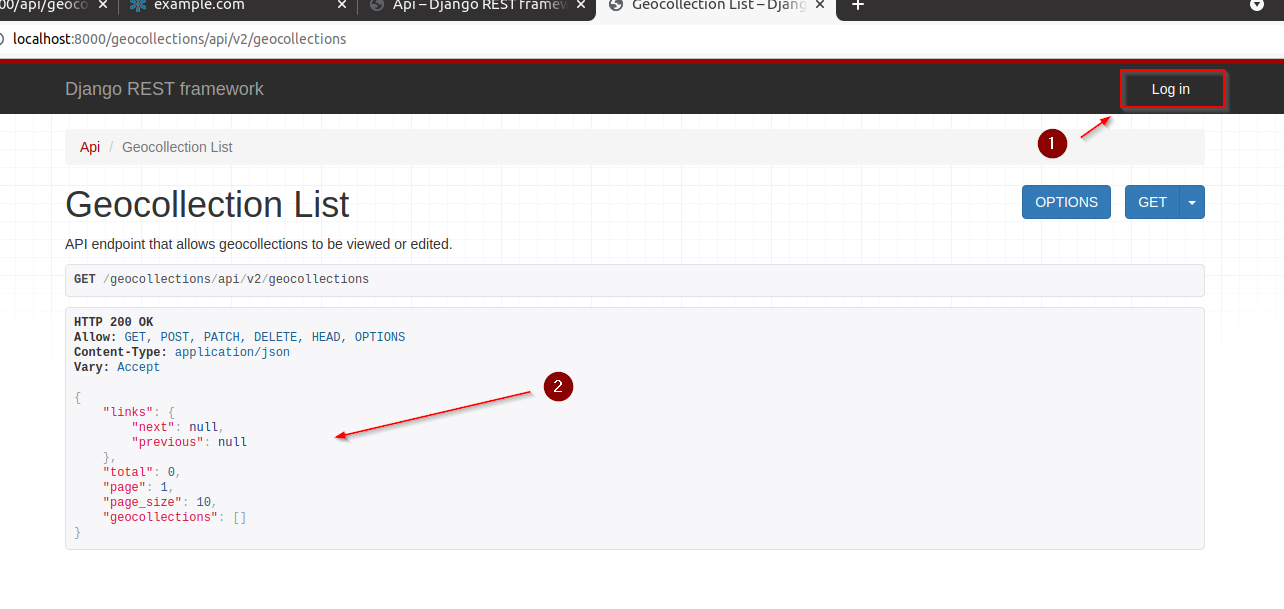
Let’s add some fancy
serializersto enable rendering the GeoNodeGroupProfileandresourcesin a more informative fashion
vim geocollections/serializers.py
Here’s the new serializers file
--- geocollections/serializers.py.org 2021-09-14 14:13:09.413865444 +0100
+++ geocollections/serializers.py 2021-09-14 14:18:26.073865444 +0100
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
from dynamic_rest.serializers import DynamicModelSerializer
+from dynamic_rest.fields.fields import DynamicRelationField
+from geonode.base.api.serializers import GroupProfileSerializer, ResourceBaseSerializer
from .models import Geocollection
@@ -11,3 +13,6 @@
fields = (
'pk', 'name', 'group', 'resources'
)
+
+ group = DynamicRelationField(GroupProfileSerializer, embed=True, many=False)
+ resources = DynamicRelationField(ResourceBaseSerializer, embed=True, many=True)
As
adminnavigate tohttp://localhost:8000/api/v2/geocollections/1.json:
This is the result you should get.